|
| ÖSTERREICH | AUSTRIA |
| Bundesland: Wien | Vienna |
| 1. Bezirk: Innere Stadt | 1st district: Inner City |
The Hofburg (Imperial Palace) was the seat of the Austrian sovereigns from the 13th century up until 1918. Around 1215/1220 it became the new residence of the Babenbergs (Duke Leopold VI of Austria), and was used also by King Ottokar II and Rudolf of Habsburg, and was enlarged and extended throughout the following centuries. The Hofburgkapelle (palace chapel) was first mentioned in 1296 and was rebuilt in 1447–1449. The Schweizertrakt, which received its current form in the Renaissance period (Schweizertor gate, 1552/53), houses the world-famous treasury with the insignia of the Holy Roman Empire, the insignia of the House of Habsburg (after 1804 the insignia of the Austrian Empire) and numerous other precious items. The Stallburg stables were built 1558–1568 is home of the famous Spanish Riding School (existing since 1572), the Winterreitschule (winter riding school) was built in 1735.

 Opposite the Schweizertrakt, the Late Renaissance
Opposite the Schweizertrakt, the Late Renaissance  Amalienburg
Amalienburg
The  monument for Emperor Franz II/I [left, no. 4170, and right, no. 2509: far right]
in the centre of square in front of the Amalienburg was created by Pompeo Marchesi in 1824–1846.
monument for Emperor Franz II/I [left, no. 4170, and right, no. 2509: far right]
in the centre of square in front of the Amalienburg was created by Pompeo Marchesi in 1824–1846.
The  Leopoldinischer Trakt [left, no. 4171, and right, no. 2509: far left] was built in
1660–1666 under Emperor Leopold I. The wing was rebuilt and enlarged in 1668–1681. It houses splendidly decorated state rooms later
inhabited by Emperor Franz I and Maria Theresia which now constitute the office of the Austrian Federal President.
Leopoldinischer Trakt [left, no. 4171, and right, no. 2509: far left] was built in
1660–1666 under Emperor Leopold I. The wing was rebuilt and enlarged in 1668–1681. It houses splendidly decorated state rooms later
inhabited by Emperor Franz I and Maria Theresia which now constitute the office of the Austrian Federal President.
The Reichskanzleitrakt (Imperial chancellery tract) was built in 1723–1730 by Johann Lukas von Hildebrandt and Joseph Emanuel Fischer von Erlach.
This tract houses the state rooms used later by Emperor Franz Joseph I and Empress Elisabeth.
The Hofbibliothek (now Nationalbibliothek) was built in 1735 by Joseph Emanuel Fischer von Erlach after plans made by his father, Johann Bernhard, for
Emperor Karl VI. The side wings of the library were built by Nikolaus Pacassi in 1763–1769. The Redoutensäle halls in the right wing were destroyed by
a fire in 1992 and were restored, partly using modern designs, in 1997. The left wing incorporates the façade of the Augustine church.
 The
The  Michaelertrakt
Michaelertrakt
The Neue Hofburg was built in 1869–1913 by Gottfried Semper and Carl Hasenauer.
The Kaiserforum was planned to occupy the area between the Imperial Palace and the Imperial Stables. The plans made by Gottfried Semper were approved by Emperor Fraz-Joseph in 1870 and construction works began in the following year. The plan was not fully carried out. Only the two museums housing the Imperial collections (the Museum of Art History and the Museum of Natural History; see below) and the Neue Hofburg were completed while the northwestern wing of the Imperial Palace (opposite the Neue Hofburg) was never built. The part east of the Ringstraße towards the Imperial Palace today is known as Heldenplatz while the opposite part between the two museums bears the name Maria-Theresien-Platz.
The  Erzherzog-Karl-Denkmal [left] in Heldenplatz was created by the sculptor Anton Dominik von Fernkorn in 1853–1859.
It was the first monumental equestrian monument that is supported only by the two hind legs. The pedestal was designed by the architects Eduard van der Nüll and
August Sicard von Sicardsburg. The statue was cast in eight parts and in total weighs 20 metric tons.
Erzherzog-Karl-Denkmal [left] in Heldenplatz was created by the sculptor Anton Dominik von Fernkorn in 1853–1859.
It was the first monumental equestrian monument that is supported only by the two hind legs. The pedestal was designed by the architects Eduard van der Nüll and
August Sicard von Sicardsburg. The statue was cast in eight parts and in total weighs 20 metric tons.
Archduke Karl (1771–1847) was a younger brother of Emperor Franz II/I. On 21/22 May 1809, Karl defeated Napoleon in the battle of Aspern (today part of Vienna's 22nd district). This was the first defeat of Napoleon. However, Napoleon remained victorious in the battle of Wagram only a few weeks later (5/6 July 1809). Archduke Karl subsequently had to sign the armistice of Znaim (now Znojmo, CZ) and resigned as commander of the Austrian army. He retired to live in his palace Weilburg at Baden.
The unveiling of the monument originally was planned for the year 1859, the 50th anniversary of Archduke Karl's victory at Aspern. However, as Austria in 1859 had lost the battles of Magenta and Solferino, which caused the loss of Lombardy, the unveiling was postponed to 1860.
The  Äußeres Burgtor [left] was built in 1821–1824 in place of an older gate that had been
destroyed by French troops in 1809. The gate was remodelled in 1934 to serve as a war memorial.
Äußeres Burgtor [left] was built in 1821–1824 in place of an older gate that had been
destroyed by French troops in 1809. The gate was remodelled in 1934 to serve as a war memorial.
The buildings in the background are the
 Kunsthistorisches Museum (Museum of Art History) [background left] and the
Kunsthistorisches Museum (Museum of Art History) [background left] and the
 Naturhistorisches Museum (Museum of Natural History) [background right]. The museums
were built in 1871–1891 by the architects Gottfried Semper und Carl Hasenauer for the Imperial Collections.
Naturhistorisches Museum (Museum of Natural History) [background right]. The museums
were built in 1871–1891 by the architects Gottfried Semper und Carl Hasenauer for the Imperial Collections.
The  Maria-Theresien-Denkmal [centre foreground] marks the centre of Maria-Theresien-Platz, the park between the two monumental
Imperial museums. The monument for Maria-Theresia of Austria (born 1717, regent of Austria from 1740 until 1780, queen of Hungary and Bohemia and wife of Emperor Franz II)
was created in 1874–1888 by the sculptor Caspar von Zumbusch (who also designed the famous monument for German Emperor Wilhelm I in Porta Westfalica in Germany).
The monument has a height of 19.4 metres and, together with its pedestal, covers an area of 632 square metres.
The monument, topped by the seating figure of Maria-Theresia is surrounded by 4 equestrian statues of the generals
Leopold Joseph von Daun, Gideon Ernst von Laudon, Otto Ferdinand von Abensperg und Traun, and Ludwig Andreas von Khevenhüller. The structure is Vienna's largest monument.
Maria-Theresien-Denkmal [centre foreground] marks the centre of Maria-Theresien-Platz, the park between the two monumental
Imperial museums. The monument for Maria-Theresia of Austria (born 1717, regent of Austria from 1740 until 1780, queen of Hungary and Bohemia and wife of Emperor Franz II)
was created in 1874–1888 by the sculptor Caspar von Zumbusch (who also designed the famous monument for German Emperor Wilhelm I in Porta Westfalica in Germany).
The monument has a height of 19.4 metres and, together with its pedestal, covers an area of 632 square metres.
The monument, topped by the seating figure of Maria-Theresia is surrounded by 4 equestrian statues of the generals
Leopold Joseph von Daun, Gideon Ernst von Laudon, Otto Ferdinand von Abensperg und Traun, and Ludwig Andreas von Khevenhüller. The structure is Vienna's largest monument.
The former  Imperial Stables [background right] were built in 1713–1725 for Emperor Karl VI by the architects
Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach and his son, Joseph Emanuel Fischer von Erlach.
Although the plans were not fully executed, the historic stables are among the largest and most magnificent in Europe.
During the Napoleonic Wars the stables were heavily damages as the French troops had used the complex as their headquarters which consequently were bombarded by the Austria troops.
Renovations and further additions followed after 1829. Following further damages during the Austrian Revolution of 1848, further additions carried out in 1850 included the
indoor riding school in Neo-Baroque style. After World War I and the dissolution of the Austria Empire the stables lost their function and most of its components were sold off.
In 1921 the complex was first used as an exhibition and trade fair venue and in the following years was developed to become Vienna's 'Messepalast', the central trade fair venue.
Between 1980 and 1986 the first plans for a redevelopment as a museum district were drawn up. Construction works for the new Museumsquartier started in 1998 and
were completed in 1991. Within the historic complex, the Museumsquartier now also he contemporary museum buildings MUMOK (Museum Moderner Kunst Stiftng Ludwig Wien) and
Leopold Museum. These two museums and the Kunsthalle in the riding school are the three largest museums in the Museumsquartier which currently is the world's
eighth-largest cultural centre.
Imperial Stables [background right] were built in 1713–1725 for Emperor Karl VI by the architects
Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach and his son, Joseph Emanuel Fischer von Erlach.
Although the plans were not fully executed, the historic stables are among the largest and most magnificent in Europe.
During the Napoleonic Wars the stables were heavily damages as the French troops had used the complex as their headquarters which consequently were bombarded by the Austria troops.
Renovations and further additions followed after 1829. Following further damages during the Austrian Revolution of 1848, further additions carried out in 1850 included the
indoor riding school in Neo-Baroque style. After World War I and the dissolution of the Austria Empire the stables lost their function and most of its components were sold off.
In 1921 the complex was first used as an exhibition and trade fair venue and in the following years was developed to become Vienna's 'Messepalast', the central trade fair venue.
Between 1980 and 1986 the first plans for a redevelopment as a museum district were drawn up. Construction works for the new Museumsquartier started in 1998 and
were completed in 1991. Within the historic complex, the Museumsquartier now also he contemporary museum buildings MUMOK (Museum Moderner Kunst Stiftng Ludwig Wien) and
Leopold Museum. These two museums and the Kunsthalle in the riding school are the three largest museums in the Museumsquartier which currently is the world's
eighth-largest cultural centre.

The  Burgtheater [left] is certainly the most famous and prestigious theater in Austria.
Its history goes back to 1741, when Maria Theresia of Austria gave permission to convert a ballroom within the Imperial palace into a theatre.
This Theater nächst der Burg opened in 1748. In 1776 Emperor Joseph II declared the theatre the
Nationaltheater nächst der Burg and entrusted a joint committee of actors and directors with its management.
Thus, 1776 is generally considered the date of the foundation of the Burgtheater as a proper theatre. The old theatre closed in 1888
and moved to the new representative building (Kaiserlich-königliches Hofburgtheater) which was designed by the architects
Gottfried Semper and Carl von Hasenauer. Due to bad acoustics the auditorium had to be remodelled in 1897. Most of the auditorium of the
theatre was destroyed in 1945 by a bomb raid and by a further fire one month later. After the war, the Burgtheater company temporarily
moved to the Varieté Ronacher. The Burgtheater was rebuilt in 1953–1955.
Burgtheater [left] is certainly the most famous and prestigious theater in Austria.
Its history goes back to 1741, when Maria Theresia of Austria gave permission to convert a ballroom within the Imperial palace into a theatre.
This Theater nächst der Burg opened in 1748. In 1776 Emperor Joseph II declared the theatre the
Nationaltheater nächst der Burg and entrusted a joint committee of actors and directors with its management.
Thus, 1776 is generally considered the date of the foundation of the Burgtheater as a proper theatre. The old theatre closed in 1888
and moved to the new representative building (Kaiserlich-königliches Hofburgtheater) which was designed by the architects
Gottfried Semper and Carl von Hasenauer. Due to bad acoustics the auditorium had to be remodelled in 1897. Most of the auditorium of the
theatre was destroyed in 1945 by a bomb raid and by a further fire one month later. After the war, the Burgtheater company temporarily
moved to the Varieté Ronacher. The Burgtheater was rebuilt in 1953–1955.



The  Parlament (originally Reichsrathsgebäude) was built in 1873–1883 by Theophil von Hansen in Neo-Renaissance style with austere classical elements.
Between 1883 and 1918 it was the seat of the upper chamber of the Reichsrat (Imperial Council) and the Abgeordnetenhaus (House of Representatives). In the First Republic
it housed the Nationalrat (National Council) and the Bundesrat (Federal Council) and between 1934 and 1938 was called Haus der Bundesgesetzgebung
(House of Federal Legislation). The building was severely damaged in 1945 and was rebuilt after the war. Today it again houses the two chambers of
the Austrian parliament, Nationalrat and Bundesrat.
Parlament (originally Reichsrathsgebäude) was built in 1873–1883 by Theophil von Hansen in Neo-Renaissance style with austere classical elements.
Between 1883 and 1918 it was the seat of the upper chamber of the Reichsrat (Imperial Council) and the Abgeordnetenhaus (House of Representatives). In the First Republic
it housed the Nationalrat (National Council) and the Bundesrat (Federal Council) and between 1934 and 1938 was called Haus der Bundesgesetzgebung
(House of Federal Legislation). The building was severely damaged in 1945 and was rebuilt after the war. Today it again houses the two chambers of
the Austrian parliament, Nationalrat and Bundesrat.

Glass no. 0000 [near left] shows a view of the parliament building with the black and yellow flag of the
Habsburg monarchy. The colours black and yellow were used as the civil flag of the Habsburg monarchy 1700–1806, as the
merchant ensign of the Habsburg monarchy 1730–1750, as the civl flag of the Austrian half ('Cisleithania') of
Austria-Hungary 1867–1918, and as the House colours of the House of Habsburg 1867–1918.
[https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flagge_%C3%96sterreichs#/media/Datei:Flag_of_the_Habsburg_Monarchy.svg]


Austria's First Republic was proclaimed on the steps of the parliament on 12 November 1918.
The stretch of the  Ringstraße
Ringstraße

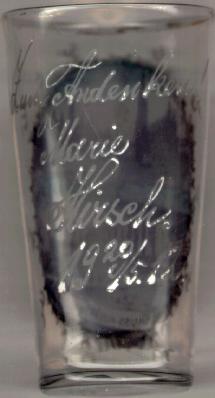




The  Rathaus (Town Hall) was built in 1872–1883 in Neogothic style
by the architect Friedrich von Schmidt who had won an international competition for the building.
The height of the middle tower had been limited to 98 m so as not to surmount the towers of the nearby Votivkirche (99 m; see below).
The statue of the Rathausmann, an armoured knight carrying a lance, on top of the tower is 3.4 m high, so that the town hall
in the end overtopped the church in height.
Rathaus (Town Hall) was built in 1872–1883 in Neogothic style
by the architect Friedrich von Schmidt who had won an international competition for the building.
The height of the middle tower had been limited to 98 m so as not to surmount the towers of the nearby Votivkirche (99 m; see below).
The statue of the Rathausmann, an armoured knight carrying a lance, on top of the tower is 3.4 m high, so that the town hall
in the end overtopped the church in height.
The square in front of the town hall is named Dr.-Karl-Lueger-Platz [see glass no. 884 below] for Karl Lueger, who had been mayor of Vienna between 1897 and 1910. Lueger is best known as a charismatic and popular politician, but he also displayed anti-semitic tendencies in conflicts with his political opponents. (Before he finally became mayor, Emperor Franz Joseph I refused to accept his election three times.) On the other hand he was responsible for considerable communal achievements during his term (gas and electricity supply, the "Green belt" forest and meadow reserve around large parts of Vienna, the 2nd water supply pipeline, social welfare and public transport). Most of the square is occupied by a park (Rathauspark).








The  Staatsoper (State Opera) was built in Neo-Romantic style 1861–1869 by August Sicard von Sicardsburg and Eduard von der Nüll
as the first monumental representative building on the Ringstraße, which had been laid out after the old fortifications of the city had been torn down.
The architecture of the opera house was severely criticized at the time, which caused the suicide of van der Nüll in 1868, and the death of Sicardsburg from a heart attack only two months later.
The predecessors of the State Opera (Kaiserlich-Königliche Hofoper) was the 'Kärntnertortheater, which had been built in 1709 and was located
behind the State Opera approximately at the site of today's famous Hotel Sacher. The State Opera was heavily damaged by a bomb raid and fire in 1945. Only
the foyer and the loggia, with frescoes by Moritz von Schwind, the main stairways, the vestibule and the tea room were spared. Almost the entire décor and properties,
the equipment for more than 120 operas with around 150,000 costumes were destroyed. Already on 6 October 1945, the State Opera opened its temporary stages
at the Theater an der Wien and at the Volkoper. The State Opera was reconstructed between 1948 and 1955, and re-opened on 5 November 1955.
Among its directors were Gustav Mahler (1897–1907), Richard Strauss (1919–1924), Clemens Krauss (1929–1934),
Karl Böhm (1943–1945), Herbert von Karajan (1956–1964) and Lorin Maazel (1982–1984).
Staatsoper (State Opera) was built in Neo-Romantic style 1861–1869 by August Sicard von Sicardsburg and Eduard von der Nüll
as the first monumental representative building on the Ringstraße, which had been laid out after the old fortifications of the city had been torn down.
The architecture of the opera house was severely criticized at the time, which caused the suicide of van der Nüll in 1868, and the death of Sicardsburg from a heart attack only two months later.
The predecessors of the State Opera (Kaiserlich-Königliche Hofoper) was the 'Kärntnertortheater, which had been built in 1709 and was located
behind the State Opera approximately at the site of today's famous Hotel Sacher. The State Opera was heavily damaged by a bomb raid and fire in 1945. Only
the foyer and the loggia, with frescoes by Moritz von Schwind, the main stairways, the vestibule and the tea room were spared. Almost the entire décor and properties,
the equipment for more than 120 operas with around 150,000 costumes were destroyed. Already on 6 October 1945, the State Opera opened its temporary stages
at the Theater an der Wien and at the Volkoper. The State Opera was reconstructed between 1948 and 1955, and re-opened on 5 November 1955.
Among its directors were Gustav Mahler (1897–1907), Richard Strauss (1919–1924), Clemens Krauss (1929–1934),
Karl Böhm (1943–1945), Herbert von Karajan (1956–1964) and Lorin Maazel (1982–1984).


The  Stephansdom (St. Stephen's Cathedral) is one of the most important churches of the High and Late Gothic period in Central Europe.
Characteristic are the lateral position of the two towers, the integration of the Romanesque western façade, the hall choir of the High Gothic period, and the
impressive steep roof covered with a decorative pattern of glazed tiles. The church measures 107 m in length, the south tower has a height of nearly 137 m.
When Vienna finally was granted the status of a diocese in 1469, St. Stephen's became a cathedral. Since 1723 it is the
metropolitan church of the archdiocese of Vienna.
Stephansdom (St. Stephen's Cathedral) is one of the most important churches of the High and Late Gothic period in Central Europe.
Characteristic are the lateral position of the two towers, the integration of the Romanesque western façade, the hall choir of the High Gothic period, and the
impressive steep roof covered with a decorative pattern of glazed tiles. The church measures 107 m in length, the south tower has a height of nearly 137 m.
When Vienna finally was granted the status of a diocese in 1469, St. Stephen's became a cathedral. Since 1723 it is the
metropolitan church of the archdiocese of Vienna.

The oldest parts of the church (the lower floors of the west towers called Heidentürme, heathens' towers) already were part of the first church which
had been built in 1137–1160.
The original church was replaced by a new, Romanesque, church between 1230 and 1263. From this church, the impressive west façade with the Riesentor
(Giant's Gate), the upper floors of the west towers and the west chancel are still extant. The construction of the three-aisled hall choir between 1304 and 1340 marked the
beginning of the Gothic period. In 1359, the foundations for the nave, a staggered hall, the two-storied chapels on the west side, and the construction of the south tower
(Hoher Turm, high tower) were laid out. The south tower (137 m high) was finished by Hans of Prachatitz (Prachatice, CZ) in 1433.
The vaulting of the nave was completed by Hanns Puchspaum (Puchsbaum) in 1446. The attic, a masterpiece of Gothic carpentry was destroyed in 1945, and was reconstructed in steel on the model of the original after the war.
Puchspaum also created the vestibule of the Singertor (before 1450) and designed the north tower (Adlerturm, eagle's tower).
The construction of the north tower started in 1467, but was discontinued in 1511, and was finally topped with a bell-shaped dome (height of the north tower: 61 m).
Anton Pilgram was the master-builder of St Stephen's from 1510 until 1514.
Only during the 19th century some additions and alterations were made by Friedrich von Schmidt.
In 1945, St. Stephen's Cathedral was heavily damaged by bombs and by fire. Immediately after the war, the church was reconstructed. The nave was
finished in 1952, the large new organ and the bells were finally dedicated in 1960.

Among the many treasures of art within the church are the stone-carved pulpit of the late 15th century with the famous self-portrait of Anton Pilgram (1513/1515), the Wiener Neustädter Altar (1447, purchased from the monastery of Neukloster at Wiener Neustadt in 1884), and the red marble tomb of Emperor Friedrich III (1467–1513, designed and begun by Niclas Gerhaert van Leyden). The Maria-Pötsch-Altar holds the painting of the Weeping Madonna, which was brought to St. Stephen's cathedral from Máriapócs in Hungary in 1697. Until 1945 it was exhibited in the high altar.
The north tower holds the Pummerin, the largest bell of Austria. The bell was originally cast in 1711 after the second siege of Vienna by the Turks (1683)
out of the metal of Turkish canons. It originally weighed 22,511 kg and had hung in the south tower. The bell was destroyed in 1945.
The present bell was cast in 1951 out of the metal of the old bell. It weighs 21,383 kg and thus is the second-largest bell in western Europe (after that of the cathedral of
Cologne) and the fifth-largest bell in the world. Since 1957 it hangs in the north tower. It is rung only at the principal feast days of the
ecclesiastical calendar (Easter night, Pentecost, Corpus Christi, the Assumption of the Virgin Mary, Christmas Eve), on the feast day of St. Stephen (Boxing Day),
on midnight of New Year's eve, on the death of a pope or the Archbishop of Vienna or the announcement of a new papacy or a new Archbishop of Vienna, and
on All Souls' Day for the victims of World War II.




The  Graben, an elongated square between Stock-im-Eisen-Platz/Stephansplatz and Kohlmarkt,
is situated at the site of the moat (German: Graben) that protected the southeastern wall of the Roman settlement Vindobona.
The moat was filled in around 1200. The area later served as market place for flour and vegetables, in the 17th century it was also
used as apleasureground for the Imperial court. The oldest building lining the squire is no. 11,
Palais Bartolotti-Partenfeld, built in 1720. Most other building date from the 19th century.
The
Graben, an elongated square between Stock-im-Eisen-Platz/Stephansplatz and Kohlmarkt,
is situated at the site of the moat (German: Graben) that protected the southeastern wall of the Roman settlement Vindobona.
The moat was filled in around 1200. The area later served as market place for flour and vegetables, in the 17th century it was also
used as apleasureground for the Imperial court. The oldest building lining the squire is no. 11,
Palais Bartolotti-Partenfeld, built in 1720. Most other building date from the 19th century.
The  Pestsäule
Pestsäule Leopopldsbrunnen
Leopopldsbrunnen



The bridge  Marienbrücke across the Donaukanal connecting Vienna's 1st district (Innere Stadt; Inner City) and 2nd
district (Leopoldstadt) was built in 1905/06. The bridge was rebuilt in 1951–53.
Marienbrücke across the Donaukanal connecting Vienna's 1st district (Innere Stadt; Inner City) and 2nd
district (Leopoldstadt) was built in 1905/06. The bridge was rebuilt in 1951–53.
| 2. Bezirk: Leopoldstadt | 2nd district: Leopoldstadt |

The Prater (from Latin pratum = meadow, pasture) is a large park in the
area of the previous pastures of the river Danube. The first written mention
in a document dates from 1403. Since 1560 is was used as hunting grounds for the Imperial
court. In 1766 it was opened to the public by Emperor Joseph II.
The original character of a pasture was changed to that of a park when the course
of the Danube in Vienna was straightened in 1869–1875. The amusement park
(Volksprater, also called Wurstelprater after the comical figure Hans Wurst)
in the western part of the Prater has been popular ever since around 1800.

The  Riesenrad ('Giant Wheel') (65 m high)
was erected in 1896/97 after a plan of the English engineers Walter B. Bassett and H. Hitchins.
The picture on glass no. 099 [left] shows the original shape of the
wheel with 30 cars. In 1945 they were destroyed by fire. After the war only 15 cars
were mounted on the wheel as the steel cable construction had been weakened by the fire.
Ferris wheels were invented by the Pittsburgh engineer George Washington Gale Ferris who built the
first wheel (76 m high with 36 cars) for the World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago 1893.
Of all the giant Ferris wheels built around the turn of the century (Chicago, London, Blackpool, Paris, Vienna etc.)
the Riesenrad in Vienna is the only one that has not been scrapped and is still in use.
Riesenrad ('Giant Wheel') (65 m high)
was erected in 1896/97 after a plan of the English engineers Walter B. Bassett and H. Hitchins.
The picture on glass no. 099 [left] shows the original shape of the
wheel with 30 cars. In 1945 they were destroyed by fire. After the war only 15 cars
were mounted on the wheel as the steel cable construction had been weakened by the fire.
Ferris wheels were invented by the Pittsburgh engineer George Washington Gale Ferris who built the
first wheel (76 m high with 36 cars) for the World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago 1893.
Of all the giant Ferris wheels built around the turn of the century (Chicago, London, Blackpool, Paris, Vienna etc.)
the Riesenrad in Vienna is the only one that has not been scrapped and is still in use.
The tallest modern operating Ferris wheels as of 2023 are in
Las Vegas, Nevada, ('The High Roller': 168 m with 28 cabins, opened in March 2014),
Singapore ('Singapore Flyer': 165 m with 28 cabins, opened in February 2008),
Nanchang, China, ('Star of Nanchang': 160 m with 61 cabins, opened in May 2006)
and London ('Millenium Wheel' or 'London Eye': 135 m high with 32 cabins, opened in March 2000).
The Ain Dubai, opened in 2021, is currently the tallest Ferris Wheel with a height of 250 metres;
however, is ceased operating already in 2022.
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wiener_Riesenrad, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ferris_wheel, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ain_Dubai]

The  monument for Wilhelm von Tegetthoff [left no. 3744] was created by
the architect Carl von Hasenauer and the sculptor Carl Kundmann in 1886. Wilhelm Tegetthoff (1827–1871) was
vice-admiral and commander of the Austrian-Hungarian navy. He is best-known for his achievements in the Second Schleswig War
(1864) for lifting the blockade of the Elbe and Weser ports, and in the Seven Weeks' War against Italy (1866) for his
victory in the Battle of Lissa. The monument consists of a 5-metres-high pedestal, surrounded by fighting hippocamps,
a marble column (11 metres) and a bronze sculpture of the admiral (3.5 metres). The munument was restored in
2016–2018.
monument for Wilhelm von Tegetthoff [left no. 3744] was created by
the architect Carl von Hasenauer and the sculptor Carl Kundmann in 1886. Wilhelm Tegetthoff (1827–1871) was
vice-admiral and commander of the Austrian-Hungarian navy. He is best-known for his achievements in the Second Schleswig War
(1864) for lifting the blockade of the Elbe and Weser ports, and in the Seven Weeks' War against Italy (1866) for his
victory in the Battle of Lissa. The monument consists of a 5-metres-high pedestal, surrounded by fighting hippocamps,
a marble column (11 metres) and a bronze sculpture of the admiral (3.5 metres). The munument was restored in
2016–2018.
[https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tegetthoff-Denkmal, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wilhelm_von_Tegetthoff]
| 3. Bezirk: Landstraße | 3rd district: Landstraße |

The Belvedere was created by Prince Eugène (Eugen) of Savoy (1663–1736) as his summer residence in Vienna.
The name, which refers to the splendid view on Vienna, however, originated later in the times of Maria Theresia of Austria (1717–1780).
The lower palace (Unteres Belvedere) was built in 1714–1716. The construction of the upper palace
 Oberes
Oberes
| 4. Bezirk: Wieden | 4th district: Wieden |


The  Karlskirche was built by Emperor Karl VI
after the plague of 1713. It is dedicated to St. Karl Borromäus
who was frequently invoked in times of the plague. The church is one of the
most important examples of high baroque in Austria. It was started by the architect
Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach 1716–1722 and completed 1724–1739 by his son Joseph Emanuel
who also added the dome (72 m high) to the design.
The two triumphal columns (33 m high) erected 1724–1730 are decorated with scenes from the life of
St. Charles Borromeo. They are also an allusion to the Imperial status
of Karl VI as they are designed to resemble the column of Emperor Traianus in Rome.
Karlskirche was built by Emperor Karl VI
after the plague of 1713. It is dedicated to St. Karl Borromäus
who was frequently invoked in times of the plague. The church is one of the
most important examples of high baroque in Austria. It was started by the architect
Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach 1716–1722 and completed 1724–1739 by his son Joseph Emanuel
who also added the dome (72 m high) to the design.
The two triumphal columns (33 m high) erected 1724–1730 are decorated with scenes from the life of
St. Charles Borromeo. They are also an allusion to the Imperial status
of Karl VI as they are designed to resemble the column of Emperor Traianus in Rome.

| 7. Bezirk: Neubau | 7th district: Neubau |


The  Volkstheater (the original name until 1945 was Deutsches Volkstheater)
was built 1887–1889 by the architects Ferdinand Fellner and Hermann Helmer for
the citizens of Vienna as a counterpart to the Hofburgtheater. The two architects
became famous for this type of building and built more than 50 theatres and
opera houses in numerous cities in and outside the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy.
The dome of the building was destroyed in 1945 and reconstructed in 1980/81.
Volkstheater (the original name until 1945 was Deutsches Volkstheater)
was built 1887–1889 by the architects Ferdinand Fellner and Hermann Helmer for
the citizens of Vienna as a counterpart to the Hofburgtheater. The two architects
became famous for this type of building and built more than 50 theatres and
opera houses in numerous cities in and outside the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy.
The dome of the building was destroyed in 1945 and reconstructed in 1980/81.
(See also list of further buildings by Fellner and Helmer
that are depicted on glasses of this collection.)
| 9. Bezirk: Alsergrund | 9th district: Alsergrund |


The  Lichtentaler Pfarrkirche zu den heiligen vierzehn Nothelfern
(Lichtental Parish Church of the Fourteen Holy Helpers) is also known as Schubertkirche
because Franz Schubert was baptised here in 1797 and wrote several compositions for use in the church.
After the suburb Lichtental was founded at the turn of the 18th century, religious services were first held at the local brewery.
In 1711 a chapel consecrated to St. Anna was built in the middle of the new settlement. In 1712, Emperor Charles VI laid
the foundation for a church. The building was probably designed by Johann Lukas von Hildebrandt and Andrea Pozzo. The first Solemn Mass
was held in 1714, although the church was still unfinished. In 1723, Lichtental became an independent parish.
The building was completed in 1730 and consecrated to the Fourteen Holy Helpers. Facing a rapidly growing population, the church was
expanded to its present size, from 1769 to 1773. The foundation was laid by Maria Theresia.
It shows elements of the transition from Baroque to Neoclassical architecture. The plans were designed by Joseph Ritter and Thaddäus Kärner.
The second tower was finished only in 1827.
Lichtentaler Pfarrkirche zu den heiligen vierzehn Nothelfern
(Lichtental Parish Church of the Fourteen Holy Helpers) is also known as Schubertkirche
because Franz Schubert was baptised here in 1797 and wrote several compositions for use in the church.
After the suburb Lichtental was founded at the turn of the 18th century, religious services were first held at the local brewery.
In 1711 a chapel consecrated to St. Anna was built in the middle of the new settlement. In 1712, Emperor Charles VI laid
the foundation for a church. The building was probably designed by Johann Lukas von Hildebrandt and Andrea Pozzo. The first Solemn Mass
was held in 1714, although the church was still unfinished. In 1723, Lichtental became an independent parish.
The building was completed in 1730 and consecrated to the Fourteen Holy Helpers. Facing a rapidly growing population, the church was
expanded to its present size, from 1769 to 1773. The foundation was laid by Maria Theresia.
It shows elements of the transition from Baroque to Neoclassical architecture. The plans were designed by Joseph Ritter and Thaddäus Kärner.
The second tower was finished only in 1827.
Composer Franz Schubert was baptised in the church on 1 February 1797. It was here he received his first musical training. In 1814, at age 17, he was commissioned to compose a missa solemnis for the centenary of the church, his first mass in F major. He conducted its first performance on 25 September 1814. His later masses in G major, B-flat major and C major were also composed for Lichtental Church, as well as other sacred music.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lichtental_Church]
Note that glass no. 2793 also has another painting on the inside: the picture of a nude women [right]. Beer glasses of this sort, showing a nude on the inside and an unspectacular, mostly funny, picture on the outside, were produced in large quantities for "gentlemen" of that time, i.e. the late 19th and early 20th century. This particular piece is the only example that the collector has found where the outside picture is the picture of a tourist site.
 Below the front picture of the glass, the name of its owner, "R. Pfeifer.", was added as an etching.
Below the front picture of the glass, the name of its owner, "R. Pfeifer.", was added as an etching.


The  Votivkirche was built in 1855–1879 by the
architect Heinrich von Ferstel (1828–1883) in French Neogothic style in order
to commemorate the failure of the attempted assassination of the young Emperor Franz Joseph I
in 1853. The church became the garrison church of Vienna in 1862 and was
elevated to a provost church in 1878. Today it is also the church of the
university of Vienna. The two church towers have a height of 99 m.
An art-historical treasure of the church is the renaissance tomb (prior to 1546) of
Count Niklas Salm (1459–1530) who defended Vienna against the Turks in 1529. The original location of
the tomb (until 1879) was the church of St. Dorothea which had been pulled down.
Votivkirche was built in 1855–1879 by the
architect Heinrich von Ferstel (1828–1883) in French Neogothic style in order
to commemorate the failure of the attempted assassination of the young Emperor Franz Joseph I
in 1853. The church became the garrison church of Vienna in 1862 and was
elevated to a provost church in 1878. Today it is also the church of the
university of Vienna. The two church towers have a height of 99 m.
An art-historical treasure of the church is the renaissance tomb (prior to 1546) of
Count Niklas Salm (1459–1530) who defended Vienna against the Turks in 1529. The original location of
the tomb (until 1879) was the church of St. Dorothea which had been pulled down.




| 10. Bezirk: Favoriten | 10th district: Favoriten |

The  parish church Sankt Anton [left] was conceived when towards the end of the 19th century the population of Favoriten,
Vienna's 10th district, began to grow rapidly and soon was too large for a single parish. The parish was subsequently divided and St. Anton was to become
the church of the new parish. The foundation stone was laid in 1896 in the presence of Emperor Franz-Joseph I. Named for Saint Anthony of Padua,
the patron saint of Archbishop Anton Gruscha, the church was built as a mighty construction in Historicist Romanesque-Byzantine style by the architect
Franz Ritter von Neumann. The church was completed exactly six years after the start of construction. World War II caused severe damages to the church.
Although the restoration works were begun shortly after the war, it took until 1961 to complete the reconstruction. The dome of the church has a height of 48.5 m,
the two flanking towers are 51 m high, the width of the front façade is 25 m.
parish church Sankt Anton [left] was conceived when towards the end of the 19th century the population of Favoriten,
Vienna's 10th district, began to grow rapidly and soon was too large for a single parish. The parish was subsequently divided and St. Anton was to become
the church of the new parish. The foundation stone was laid in 1896 in the presence of Emperor Franz-Joseph I. Named for Saint Anthony of Padua,
the patron saint of Archbishop Anton Gruscha, the church was built as a mighty construction in Historicist Romanesque-Byzantine style by the architect
Franz Ritter von Neumann. The church was completed exactly six years after the start of construction. World War II caused severe damages to the church.
Although the restoration works were begun shortly after the war, it took until 1961 to complete the reconstruction. The dome of the church has a height of 48.5 m,
the two flanking towers are 51 m high, the width of the front façade is 25 m.
Further building designed by Franz von Neumann depicted on glasses of this collection are the church of the parish Donaufeld in Vienna (see below), the Villa Erzherzog Eugen
in Baden, and the town hall of Liberec.
| 13. Bezirk: Hietzing | 13th district: Hietzing |


The first castle on this site was bought in 1559 by Emperor Maximilian II as a hunting seat. 1683 the castle was destroyed by the Turks. Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach designed a plan for a new palace in 1688 following Versailles Palace as ideal model. However, between 1695 and 1711 only a simplified plan was realized. 1744-49 the palace was remodelled in Baroque style by Empress Maria Theresia. After the death of her husband, Emperor Franz I Stephan, several rooms were decorated in Rococo style. In 1817–1819 the façades were remodeled in Classicist style. The palace and gardens were listed as a UNESCO World Cultural heritage Site in 1996. (see also list of other UNESCO heritage sites depicted on glasses of this collection)
After the defeat of Archduke Karl by Napoleon at Wagram in 1809, the Peace of Schönbrunn stipulated that Austria had to accept the loss of Tyrol and Vorarlberg to Bavaria. Salzburg and parts of Upper Austria also had to be ceded to Bavaria. Western Carinthia, Carniola, Croatia south of the river Sava, Görz (Gorizia), Trieste, Fiume (Rijeka) and Dalmatia were lost to France, East Galicia came to Russia, West Galicia to the Duchy of Warsaw (personal union with the Kingdom of Saxony).

The park of Schloss Schönbrunn covers an area of about 2 km2 and is one of the most important and best-preserved
Baroque gardens in French style. The original layout of 1706 was completely redesigned after 1765.
The  Neptunbrunnen [left, bottom] was created by Franz Anton Zauner in 1740.
Neptunbrunnen [left, bottom] was created by Franz Anton Zauner in 1740.
The  Gloriette [left, top] is located on top of the hill, some 45 m above the lower part of the park.
The open pillared hall was created by Ferdinand von Hohenberg in 1775 as a monument for the victory of the troops of Maria Theresia against Prussia in the
Battle of Kolín in 1757.
Gloriette [left, top] is located on top of the hill, some 45 m above the lower part of the park.
The open pillared hall was created by Ferdinand von Hohenberg in 1775 as a monument for the victory of the troops of Maria Theresia against Prussia in the
Battle of Kolín in 1757.


The  parish church of Mary, Refuge of Sinners of Ober-Sankt-Veit
was first mentioned in 1365. The present church was originally built in 1433
and reconstructed after destructions in 1529 and 1683. The church was enlarged
in 1742 by adding a Baroque nave to the Gothic chancel.
parish church of Mary, Refuge of Sinners of Ober-Sankt-Veit
was first mentioned in 1365. The present church was originally built in 1433
and reconstructed after destructions in 1529 and 1683. The church was enlarged
in 1742 by adding a Baroque nave to the Gothic chancel.
The small village of Ober-Sankt-Veit gained importance when the Archbishops
of Vienna had a summer palace built here in 1742. Since 1890/92 Ober-Sankt-Veit
is part of Vienna (13th district, Hietzing).
| 14. Bezirk: Penzing | 14th district: Penzing |
Penzing is the 14th district of Vienna. It consists of the borroughs Penzing, Breitensee, Baumgarten, Hütteldorf and Hadersdorf-Weidlingau.
The area of today's 14th district (except Hadersdorf-Weidlingau) became part of Vienna in 1892 together with today's 13th district, Hietzing (except the Lainzer Tiergarten).
At that time the area was designated as Vienna's 13th district, named Hietzing. In 1938 the district was split in two parts: the part north of the river Wien
was designated as the new 14th district, named Penzing. At the same time, the former independent communities of Hadersdorf-Weidlingau and Purkersdorf
also were incorporated into Vienna as part of the 14th district. Purkersdorf became an indepemdent municipality again in 1954, while
Hadersdorf-Weidlingau remained part of Vienna-Penzing.
In 1992 and 1995 small parts of the district were reassigned to the neighbouring city districts of Rudolfsheim-Fünfhaus (15th) and Ottakring (16th).
[https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Penzing_(Wien)]

The  Kaiser-Franz-Joseph-Landwehrkaserne was built in 1901 by the architect Johann Scheiringer
as barracks of the Landwehr-Bezirkskommando Nr. 1 (Landwehr district squad no. 1) and the Landwehr-Ergänzungsbezirkskommando Nr. 1
(Landwehr complement district squad no. 1). Between 1919 and 1923 the building was used as a malaria hospital of the city of Vienna.
In 1922 it was rededicated to become a care home with a capacity for about 1,100 persons.
During Worls War II the complex served as a military hospital. After the war, it was used first by the Red Army and then by the French occupation authorities.
Already in 1946 it was used again as a care home. An infirmary was added in 1958 by the incorporation of the neighbouring St. Rochus Hospital.
The opening as "Sankt-Rochus-Heim" took place in 1961.
Today, the "Geriatriezentrum Baumgarten" is run by the Wiener Krankenanstaltenverbund (Vienna Hospital Alliance).
At a capacity of 956 beds (2001) it is the second-largest care facility both in Austria and in Vienna.
[https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geriatriezentrum_Baumgarten]
Kaiser-Franz-Joseph-Landwehrkaserne was built in 1901 by the architect Johann Scheiringer
as barracks of the Landwehr-Bezirkskommando Nr. 1 (Landwehr district squad no. 1) and the Landwehr-Ergänzungsbezirkskommando Nr. 1
(Landwehr complement district squad no. 1). Between 1919 and 1923 the building was used as a malaria hospital of the city of Vienna.
In 1922 it was rededicated to become a care home with a capacity for about 1,100 persons.
During Worls War II the complex served as a military hospital. After the war, it was used first by the Red Army and then by the French occupation authorities.
Already in 1946 it was used again as a care home. An infirmary was added in 1958 by the incorporation of the neighbouring St. Rochus Hospital.
The opening as "Sankt-Rochus-Heim" took place in 1961.
Today, the "Geriatriezentrum Baumgarten" is run by the Wiener Krankenanstaltenverbund (Vienna Hospital Alliance).
At a capacity of 956 beds (2001) it is the second-largest care facility both in Austria and in Vienna.
[https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geriatriezentrum_Baumgarten]
Glass no. 2709 is labelled "XIII. Baumgarten, k.k. Landwehr-Kaserne". Hence, the glass must date from after 1901 (the year of the construction of the
building) and before 1938 (the year when Vienna's former 13th district was split in two and Baumgarten became part of the new 14th district).


The  parish and pilgrimage church Mariabrunn
was built 1639–1645. The vestibule was added in 1729, the church tower was
erected in 1872. The church became a popular site of pilgrimages from 1616, especially
for the Imperial court of Vienna. The wooden statue of Our Lady in the high altar dates from the
first half of the 16th century.
An epitaph for the famous Baroque architect
Johann Lukas von Hildebrandt (1668–1745) was erected in the church after his death.
The kermis of Mariabrunn was portrayed by the Austrian writer Adalbert Stifter (1805–1868)
in his book "Wien und die Wiener in Bildern aus dem Leben" (1844).
parish and pilgrimage church Mariabrunn
was built 1639–1645. The vestibule was added in 1729, the church tower was
erected in 1872. The church became a popular site of pilgrimages from 1616, especially
for the Imperial court of Vienna. The wooden statue of Our Lady in the high altar dates from the
first half of the 16th century.
An epitaph for the famous Baroque architect
Johann Lukas von Hildebrandt (1668–1745) was erected in the church after his death.
The kermis of Mariabrunn was portrayed by the Austrian writer Adalbert Stifter (1805–1868)
in his book "Wien und die Wiener in Bildern aus dem Leben" (1844).
 The former monastery of the Discalced Augustinians was founded in 1636.
The famous preacher Abraham a Sancta Clara (Matthias Megerle, 1644–1709)
joined the monastery as a novice in 1662 and completed his theological studies
here in 1666. The monastery was dissolved in 1785/86.
Since 1813 it is the seat of the forestry school (founded 1805 in
Purkersdorf) which became a section of the Vienna
University for Agriculture in 1875.
The former monastery of the Discalced Augustinians was founded in 1636.
The famous preacher Abraham a Sancta Clara (Matthias Megerle, 1644–1709)
joined the monastery as a novice in 1662 and completed his theological studies
here in 1666. The monastery was dissolved in 1785/86.
Since 1813 it is the seat of the forestry school (founded 1805 in
Purkersdorf) which became a section of the Vienna
University for Agriculture in 1875.

The village of Mariabrunn became part of Vienna (14th district, Penzing) in 1938.
| 16. Bezirk: Ottakring | 16th district: Ottakring |
Ottakring is the 16th District in the city of Vienna. It is located west of the central districts,
north of Penzing (14th district) and south of Hernals (17th district). The original Ottakring was founded about 1,000 years
ago by Bavarian settlers who cleared a small patch of forest on the cityward slope of the Gallitzinberg.
The oldest written document mentioning Otachringen dates from 1147.
The “oldest Ottakring” settlement was completely destroyed in 1683 during the Battle of Vienna. The village was
rebuilt further downstream on the Ottakringer Bach, closer to Vienna. This nucleus, parts of which survived into the 1980s,
was what became known as Alt-Ottakring in the 19th and 20th century. In 1888, Emperor Franz Joseph I declared that
he wanted to unite Vienna with the surrounding villages. The Lower Austrian government passed a law, the
‘Eingemeindung der Vororten zu Wien (Annexation of Villages to Vienna)’ in 1890. On 1 January 1892, the
resolution took effect. Despite initial resistance, the independent villages of Ottakring and Neulerchenfeld were merged into
the 16th district of Vienna.
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ottakring, https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alt-Ottakringer_Pfarrkirche]
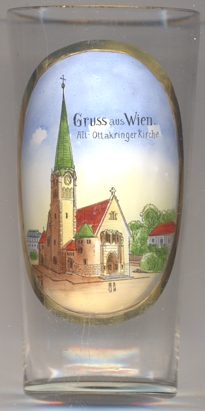
The  Alt-Ottakringer Pfarrkirche zur Erhöhung des Heiligen Kreuzes
(Parish Church of the Exaltation of the Holy Cross) [left] goes back to a church dedicated to
Alt-Ottakringer Pfarrkirche zur Erhöhung des Heiligen Kreuzes
(Parish Church of the Exaltation of the Holy Cross) [left] goes back to a church dedicated to
[https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alt-Ottakringer_Pfarrkirche]
| 17. Bezirk: Hernals | 17th district: Hernals |

The  Kalvarienbergkirche (Calvary Church of St. Bartholomew) [left]
is located in the historic centre of Hernals, which gave its name to Vienna's 17th district, Hernals.
The northern parts of the church with its main façade and tower date from the Baroque period, the
southern parts were built in Baroque revival style.
The original parish church of Hernals was first mentioned in 1301. This church was destroyed by the Turks during the First Siege of Vienna in 1529.
After having been rebuilt in 1548 or 1568 it became a Lutheran church. At that time, Protestant churches were forbidden in Vienna, so that many
Protestants went to church in Hernals, at that time an independent community owned by the Protestant Jörger family, barons of Tollet.
In 1625, during the Counter-Reformation, the church was reconverted into a Catholic church. As part of the Catholic propaganda, a Holy Sepulchre chapel in Moorish style
was built next to he church in 1639. A Via Crucis with 7 stations lead from Vienna to Hernals; the distance between St. Stephen's Cathedral and
the Chapel of the Holy Sepulchre matched the length of the Via Dolorosa in Jerusalem. The pilgrimage site, however, was closed 35 years later,
because the site had also attracted prostitutes and criminals. During the Second Siege of Vienna (1683) the parish church, the chapel and the via crucis
were largely destroyed. In 1710 the Via Crucis was recreated in Hernals, this time in the form of a Calvary. Unlike at Maria-Lanzendorf
it was not necessary to create an artificial mound as there was already a natural hill. A stairway with 7 chapels on both sides lead up the hill
which was crowned by a Crucifixion. The site was finished in 1717. Inside the hill, a small church was constructed.
Hernals again became a popular pilgrimage site. Between 1720 and 1784 the Pauline Fathers (Order of St. Paul the First Hermit) were in charge of the church,
which was rebuilt in 1766–1769. In 1784 the Calvary church became the new parish church of Hernals. Stones of the ruins of the old parish church were used to
build a new tower in 1785. The remaining parts of the church were rebuilt in 1822–1828 and in 1831.
Between 1889 and 1894 the church was enlarged by the architect Richard Jordan who created today's appearance of the church. The Baroque Stations
of the Cross — until then separate from the church — were incorporated into the building, which was extended
by its new southern parts in Baroque revival style. The church was severly hit by a bomb raid on 22 March 1945 but was rebuilt after the war.
A plaque on the church commemorates the fact that it was in this church that the famous composer Franz Schubert heard the last piece of music before
his death in 1828, the Latin Requiem of his brother, Ferdinand Schubert. The central object of veneration is the
Kalvarienbergkirche (Calvary Church of St. Bartholomew) [left]
is located in the historic centre of Hernals, which gave its name to Vienna's 17th district, Hernals.
The northern parts of the church with its main façade and tower date from the Baroque period, the
southern parts were built in Baroque revival style.
The original parish church of Hernals was first mentioned in 1301. This church was destroyed by the Turks during the First Siege of Vienna in 1529.
After having been rebuilt in 1548 or 1568 it became a Lutheran church. At that time, Protestant churches were forbidden in Vienna, so that many
Protestants went to church in Hernals, at that time an independent community owned by the Protestant Jörger family, barons of Tollet.
In 1625, during the Counter-Reformation, the church was reconverted into a Catholic church. As part of the Catholic propaganda, a Holy Sepulchre chapel in Moorish style
was built next to he church in 1639. A Via Crucis with 7 stations lead from Vienna to Hernals; the distance between St. Stephen's Cathedral and
the Chapel of the Holy Sepulchre matched the length of the Via Dolorosa in Jerusalem. The pilgrimage site, however, was closed 35 years later,
because the site had also attracted prostitutes and criminals. During the Second Siege of Vienna (1683) the parish church, the chapel and the via crucis
were largely destroyed. In 1710 the Via Crucis was recreated in Hernals, this time in the form of a Calvary. Unlike at Maria-Lanzendorf
it was not necessary to create an artificial mound as there was already a natural hill. A stairway with 7 chapels on both sides lead up the hill
which was crowned by a Crucifixion. The site was finished in 1717. Inside the hill, a small church was constructed.
Hernals again became a popular pilgrimage site. Between 1720 and 1784 the Pauline Fathers (Order of St. Paul the First Hermit) were in charge of the church,
which was rebuilt in 1766–1769. In 1784 the Calvary church became the new parish church of Hernals. Stones of the ruins of the old parish church were used to
build a new tower in 1785. The remaining parts of the church were rebuilt in 1822–1828 and in 1831.
Between 1889 and 1894 the church was enlarged by the architect Richard Jordan who created today's appearance of the church. The Baroque Stations
of the Cross — until then separate from the church — were incorporated into the building, which was extended
by its new southern parts in Baroque revival style. The church was severly hit by a bomb raid on 22 March 1945 but was rebuilt after the war.
A plaque on the church commemorates the fact that it was in this church that the famous composer Franz Schubert heard the last piece of music before
his death in 1828, the Latin Requiem of his brother, Ferdinand Schubert. The central object of veneration is the
 'Turks'
'Turks'
[https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kalvarienbergkirche_(Wien), http://www.kalvarienbergkirche.at/]

The oldest document relating to  Dornbach
Dornbach
The former inn  Zur güldenen Waldschnepfe (The Golden Woodcock) [left, no. 4624: right],
the core of which dates back to the 17th century, was built in 1883/1884. It was closed after World War II. Today it houses an office and
an Italian restaurant.
Zur güldenen Waldschnepfe (The Golden Woodcock) [left, no. 4624: right],
the core of which dates back to the 17th century, was built in 1883/1884. It was closed after World War II. Today it houses an office and
an Italian restaurant.
[https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dornbach_(Wien)]
| 19. Bezirk: Döbling | 19th district: Döbling |

Nussdorf (until 1999 spelled Nußdorf) is part of the 19th district of Döbling. The name Nuzdorf (Nussdorf, i.e. 'nut-village') was first mentioned in a document of the monastery of Klosterneuburg in 1114. In 1892, Nussdorf and the neighbouring peripheral settlements of Sievering, Grinzing, Oberdöbling, Unterdöbling, Heiligenstadt and Kahlenbergerdorf were incorporated into Vienna as a town district.
The  Nussdorfer Pfarrkiche zum Heiligen Apostel Thomas (parish church of the Apostle Thomas) [left]
goes back to a chapel dedicated to the Apostle Thomas which had been founded in the 15th century. The present church was built in 1795,
financed through the appropriation of property belonging to several religious orders by Emperor Joseph II.
Nussdorfer Pfarrkiche zum Heiligen Apostel Thomas (parish church of the Apostle Thomas) [left]
goes back to a chapel dedicated to the Apostle Thomas which had been founded in the 15th century. The present church was built in 1795,
financed through the appropriation of property belonging to several religious orders by Emperor Joseph II.
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nussdorf,_Vienna]
Another glass in this collection shows a view of
Nußdorf am Attersee in Upper Austria.
| 20. Bezirk: Brigittenau | 20th district: Brigittenau |

The  Sperrschiff (blocking ship) or Schwimmtor (floating gate) [left]
was a floating barrier designed to protect the areas along the Donaukanal (Danube Canal) in Vienna from flooding and ice. It was built by Wilhelm von Engerth,
entered service on 13 December 1873, and was scrapped following World War II. The Schwimmtor was located 166 metres downstream of the Brigittenauer Spitz,
the beginning of the Danube Canal. The site was chosen because the canal was narrow enough at this point that the floating barrier could withstand the pressure which would
be caused by an accumulation of floodwater or ice. A rounded indentation was carved into the left-hand (Brigittenau) quay wall, where the Schwimmtor was to be stowed when
it was not needed. Just downstream of this indentation, the quay wall jutted out into the middle of the canal, thereby forming a support against which the barrier could be
placed when it was needed. On the other bank, a niche was carved into the quay wall housing two moveable steel barriers (the Stemmtor and the Anlagetor). The Schwimmtor
remained in service even after the construction of a weir and lock in Nussdorf, but fell out of use during World War I and was finally scrapped after World War II.
The rounded indentation in the quay wall on the Brigittenau bank, the supporting wall jutting out into the canal, and the niche in the wall on the Nussdorf side of the canal
have all survived to the modern day. The capstan which was used to move the Stemmtor and Anlagetor has also been preserved.
Sperrschiff (blocking ship) or Schwimmtor (floating gate) [left]
was a floating barrier designed to protect the areas along the Donaukanal (Danube Canal) in Vienna from flooding and ice. It was built by Wilhelm von Engerth,
entered service on 13 December 1873, and was scrapped following World War II. The Schwimmtor was located 166 metres downstream of the Brigittenauer Spitz,
the beginning of the Danube Canal. The site was chosen because the canal was narrow enough at this point that the floating barrier could withstand the pressure which would
be caused by an accumulation of floodwater or ice. A rounded indentation was carved into the left-hand (Brigittenau) quay wall, where the Schwimmtor was to be stowed when
it was not needed. Just downstream of this indentation, the quay wall jutted out into the middle of the canal, thereby forming a support against which the barrier could be
placed when it was needed. On the other bank, a niche was carved into the quay wall housing two moveable steel barriers (the Stemmtor and the Anlagetor). The Schwimmtor
remained in service even after the construction of a weir and lock in Nussdorf, but fell out of use during World War I and was finally scrapped after World War II.
The rounded indentation in the quay wall on the Brigittenau bank, the supporting wall jutting out into the canal, and the niche in the wall on the Nussdorf side of the canal
have all survived to the modern day. The capstan which was used to move the Stemmtor and Anlagetor has also been preserved.
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schwimmtor]
| 21. Bezirk: Floridsdorf | 21st district: Floridsdorf |

 The
The  church of Sankt Leopold, church of the parish Donaufeld,
was built in 1905–1914 Neo-Gothic style by the architect Franz von Neumann.
Before 1905 Floridsdorf was not yet part of Vienna and there had been plans to make the Floridsdorf
the capital of Lower Austria. The church thus was designed to become the seat of a new diocese.
The plans did not become reality so that the large church in 1914 became the parish church of the
newly established parish of Donaufeld. The church spire (96 m) is the third-highest in Vienna after the spires
of St. Stephen's Cathedral and the Votivkirche (both above). St. Leopold is also the third-largest church
of Vienna in terms of capacity after St. Stephen's and the church Am Hof.
church of Sankt Leopold, church of the parish Donaufeld,
was built in 1905–1914 Neo-Gothic style by the architect Franz von Neumann.
Before 1905 Floridsdorf was not yet part of Vienna and there had been plans to make the Floridsdorf
the capital of Lower Austria. The church thus was designed to become the seat of a new diocese.
The plans did not become reality so that the large church in 1914 became the parish church of the
newly established parish of Donaufeld. The church spire (96 m) is the third-highest in Vienna after the spires
of St. Stephen's Cathedral and the Votivkirche (both above). St. Leopold is also the third-largest church
of Vienna in terms of capacity after St. Stephen's and the church Am Hof.
The old name of the Floridsdorf area was Am Spitz. In 1786 it was renamed Floridsdorf for
Floridus Leeb, abbot of Klosterneuburg, who had donated grounds for a new settlement.
The first houses in the Donaufeld area were built in the early 1860's. At first the area received the name Neu-Leopoldau,
but in 1885 the name Donaufeld was introduced and was made official in 1886.
In 1895 Donaufeld was merged with Floridsdorf (1894 incorporated as a town), Neu-Jedlersdorf and Jedlesee to become the municipality of Floridsdorf.
In 1904 Floridsdorf became part of Vienna (21st district) together with Leopoldau, Kagran, Hirschstetten, Stadlau and Aspern,
and in 1910 it was expanded by the incorporation of Strebersdorf. In 1938 Kagran, Stadlau, Hirschstetten, Aspern and
the Lobau area were separated from Floridsdorf to become the 22nd district, Donaustadt.
In 1954 the boundary between the 21st and 22nd district was rearranged, and Stammersdorf was incorporated into Floridsdorf.
| 23. Bezirk: Liesing | 23rd district: Liesing |
 Liesing proper, today a cadastral district of Vienna's district, is situated on both sides of the river Liesing. The river
was first mentioned (as Liezniccha) in 1002. The name likely is derived from the Slavic Lesnička ('forest stream'). The settlement
most likely began to develop at about the same time. Mostly destroyed during the First (1529) and Second (1683) Sieges of Vienna by the Ottomans, it had
to be resettled. In the follwoing period, however, it son became one the most important settlements of the area. Up until the 19th century, it had
a mostly rural character. Indutrialisation started in 1838 with the founding of the Liesing brewery. In 1905 Liesing obtained the official status of a
town. Plans to merge Liesing with Atzgersdorf (1920) or with Atzgersdorf, Erlaa and Siebenhirten (1929) were finally unseccessful. On 1 October 1938,
many municipalities surrounding what was then the city of Vienna were incorporated into the city to become Groß-Wien (Greater Vienna). The
former southern suburbs were grouped into the new XXV district, also named Liesing as this was the most central of the former municpalities
in this district. After World War II Greater Vienna was dissolved again, but Liesing, together with 7 further former municipalities (Atzgersdorf,
Erlaa, Inzersdorf, Kalksburg (see below), Mauer (see below), Rodaun and Siebenhirten) remained with Vienna; these parts now form Vienna's 23rd district, Liesing.
Liesing proper, today a cadastral district of Vienna's district, is situated on both sides of the river Liesing. The river
was first mentioned (as Liezniccha) in 1002. The name likely is derived from the Slavic Lesnička ('forest stream'). The settlement
most likely began to develop at about the same time. Mostly destroyed during the First (1529) and Second (1683) Sieges of Vienna by the Ottomans, it had
to be resettled. In the follwoing period, however, it son became one the most important settlements of the area. Up until the 19th century, it had
a mostly rural character. Indutrialisation started in 1838 with the founding of the Liesing brewery. In 1905 Liesing obtained the official status of a
town. Plans to merge Liesing with Atzgersdorf (1920) or with Atzgersdorf, Erlaa and Siebenhirten (1929) were finally unseccessful. On 1 October 1938,
many municipalities surrounding what was then the city of Vienna were incorporated into the city to become Groß-Wien (Greater Vienna). The
former southern suburbs were grouped into the new XXV district, also named Liesing as this was the most central of the former municpalities
in this district. After World War II Greater Vienna was dissolved again, but Liesing, together with 7 further former municipalities (Atzgersdorf,
Erlaa, Inzersdorf, Kalksburg (see below), Mauer (see below), Rodaun and Siebenhirten) remained with Vienna; these parts now form Vienna's 23rd district, Liesing.
[https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liesing_(Wiener_Bezirksteil)]
The  Liesing Brewery [left, no. 4450: centre] was founded in 1838 and started operating in the following
year as Ober-Liesinger Felsenkeller-Bräu. Since 1872 it operated as a public limited company, Aktiengesellschaft der Liesinger Brauerei
(or short, Aktienbrauerei Liesing). The small tower depicted on glass no. 4450 [left] was built in 1898 by the architects
Helmer and Fellner (see a list of their buildings) and soon became the brewery's popular landmark. In 1928 the brewery
was merged with the Österreichische Brau-AG. The brewery ended its operations in 1973. In the 1990s, parts of the brewery area were used as a
market area for flea markets. After a spectacular major fire oin 2005, these activities were also stopped and demolition work began. From 2008 to 2012,
more than 450 apartments, a shopping center, a dormitory and a daycare center were built on the ten-hectare brewery site.
Liesing Brewery [left, no. 4450: centre] was founded in 1838 and started operating in the following
year as Ober-Liesinger Felsenkeller-Bräu. Since 1872 it operated as a public limited company, Aktiengesellschaft der Liesinger Brauerei
(or short, Aktienbrauerei Liesing). The small tower depicted on glass no. 4450 [left] was built in 1898 by the architects
Helmer and Fellner (see a list of their buildings) and soon became the brewery's popular landmark. In 1928 the brewery
was merged with the Österreichische Brau-AG. The brewery ended its operations in 1973. In the 1990s, parts of the brewery area were used as a
market area for flea markets. After a spectacular major fire oin 2005, these activities were also stopped and demolition work began. From 2008 to 2012,
more than 450 apartments, a shopping center, a dormitory and a daycare center were built on the ten-hectare brewery site.
[https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brauerei_Liesing]

Mauer is a cadastral community located in the northwest of Vienna's 23rd district, Liesing. Archeological finds demonstrate that the
area had already been inhabited in prehistoric times. Remnants of a jasper mine were dated to about 4000 BC. The oldest known written mention
dates from 1210. Wine production began during the Middle Ages, and still continues today. In 1609 the vilage came in possession of the Jesuits
who remained the owners until 1773. In Biedermeier times Mauer was a famous Viennese summer retreat location. The first mayor took office in 1850,
and the village was promoted to market town in 1902. After Nazi Germany annexed Austria, the City of Vienna was expanded greatly, which led to the
incorporation of Mauer in 1938 (see map). The Rosenhügel Film Studios, which were built from 1919 to 1923 in the north
of Mauer, were considered at their opening as the most modern and largest film studios in Austria. Almost all buildings were demolished in 2016.
[https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mauer_(Wien), https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mauer,_Vienna]
The  church of Sankt Erhard [left, no. 4206: background] became Mauer's parish church only in 1783.
Before that, Mauer had been part of the parish of neighbouring Atzgersdorf. The church itself had already been built in the mid-15th century and
was mentioned for the first time in 1458. From its beginnings, the church had been laid out as a fortified chapel. Nevertheless, it can bee assumed
that it suffered severe damages during the times of the Ottoman sieges of Vienna (1529, 1683). As in the aearly 20th century the building with
its east–west orientation had become an obstacle for the newly built tram lines, the church was extensively modified in 1934–1936 by the
architect Clemens Holzmeister. During this reconstruction, the entire nave was pulled down and the church was given a north–south orientation.
Of the old building structure, the Gothic choir, which was repurposed as a side chapel, and the medieval church tower with its tower dome from 1770
remain. The new glass windows were designed by the painter Albert Paris Gütersloh.
church of Sankt Erhard [left, no. 4206: background] became Mauer's parish church only in 1783.
Before that, Mauer had been part of the parish of neighbouring Atzgersdorf. The church itself had already been built in the mid-15th century and
was mentioned for the first time in 1458. From its beginnings, the church had been laid out as a fortified chapel. Nevertheless, it can bee assumed
that it suffered severe damages during the times of the Ottoman sieges of Vienna (1529, 1683). As in the aearly 20th century the building with
its east–west orientation had become an obstacle for the newly built tram lines, the church was extensively modified in 1934–1936 by the
architect Clemens Holzmeister. During this reconstruction, the entire nave was pulled down and the church was given a north–south orientation.
Of the old building structure, the Gothic choir, which was repurposed as a side chapel, and the medieval church tower with its tower dome from 1770
remain. The new glass windows were designed by the painter Albert Paris Gütersloh.
[https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pfarrkirche_Mauer]

The village of Kalksburg is situated on the Liesingbach stream, and is part of Vienna's 23rd district, Liesing.
The Jesuit school, founded in 1856, was nicknamed 'the Oxford of the Old Monarchy'. Kalksburg was an independent municipality until 1938 when it
became part of 'Groß-Wien' (Greater Vienna).

The  “Devil's Mill” (Teufelsmühle) on the Wienerberg on the road from Vienna to Wiener Neustadt was already mentioned in 1477.
An old legend tells the story of the owner, a cruel man who killed his pious wife by
throwing her into the mill's well when she criticized his evil way of life. For a long time the spirits of the two haunted the mill. A long time later a noble knight took
shelter in the haunted mill. In the middle of the knight the ghost of the wife appeared and asked the knight to recover her body from the bottom of the well and
bury her in blessed ground. When he did so the next morning the haunted spirits of the man and his wife found peace and the knight is said to have found a
large fortune when he returned to his home.
The mill was destroyed by fire in 1902. After that it was rebuilt as a country inn [right, no. 726].
It still serves as a restaurant today and bears the name “Gasthaus zur Teufelsmühle”.
“Devil's Mill” (Teufelsmühle) on the Wienerberg on the road from Vienna to Wiener Neustadt was already mentioned in 1477.
An old legend tells the story of the owner, a cruel man who killed his pious wife by
throwing her into the mill's well when she criticized his evil way of life. For a long time the spirits of the two haunted the mill. A long time later a noble knight took
shelter in the haunted mill. In the middle of the knight the ghost of the wife appeared and asked the knight to recover her body from the bottom of the well and
bury her in blessed ground. When he did so the next morning the haunted spirits of the man and his wife found peace and the knight is said to have found a
large fortune when he returned to his home.
The mill was destroyed by fire in 1902. After that it was rebuilt as a country inn [right, no. 726].
It still serves as a restaurant today and bears the name “Gasthaus zur Teufelsmühle”.
The village of Siebenhirten became part of Vienna (25th district [see inscription on the glass], Liesing) in 1938 when a total of 96 municipalities were incorporated into
the city of Vienna. In 1954, 80 of these former villages were returned to Lower Austria again. The district Liesing with Siebenhirten, however, remained part of Vienna (now 23rd district).
![[scale]](lineal.jpg)